In this article, we are going to learn how to code Calendar using Java. The calendar application is occasionally asked in interviews to be built by the candidate. If you are intermediate in Java, it helps to improve your coding skills also, it is interesting to make this application. Let’s get started!
Calendar class in Java
Calendar class is an abstract class in Java that provides methods for multiple operations such as displaying the year, month, day, hour, etc. It inherits the Object class and implements the Comparable, Serializable, and Cloneable interfaces.
Calendar’s getInstance method returns a Calendar object whose calendar fields have been initialized with the current date and time:
Calendar rightNow = Calendar.getInstance();A Calendar object can produce all the calendar field values needed to implement the date and time formatting for a particular language and calendar style. The calendar field values can be set by calling the set methods. Any field values set in a Calendar will not be interpreted until it needs to calculate its time value or the values of the calendar fields.
The calendar has two modes for interpreting the calendar fields, lenient and non-lenient. When a Calendar is in lenient mode, it accepts a broader range of calendar field values than it produces. When a Calendar is in non-lenient mode, it throws an exception if there is any inconsistency in its calendar fields.
The date or time format strings are not part of the definition of a calendar, as those must be modifiable or overridable by the user at runtime.
Calendar methods in Java
There is a bundle of Calendar methods available in Java. These methods are used for a wide range of functions with Calendar using java. Let’s take a look at those methods in the following section.
| S.No | Method Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | abstract void add(int field, int amount) | This method adds or subtracts the specified amount of time to the given calendar field, based on the calendar’s rules |
| 2 | boolean after(Object when) | This method returns whether the Calendar represents a time after the time represented by the specified Object |
| 3 | boolean before(Object when) | This method returns whether the Calendar represents a time before the time represented by the specified Object. |
| 4 | void clear() | This method sets all the calendar field values and the time value of the Calendar undefined |
| 5 | void clear(int field) | This method sets the given calendar field value and the time value of the Calendar undefined |
| 6 | Object clone() | This method creates and returns a copy of the object |
| 7 | int compareTo(Calendar anotherCalendar) | This method compares the time values represented by two Calendar objects |
| 8 | protected void complete() | This method fills in any unset fields in the calendar fields. |
| 9 | protected abstract void computeFields() | This method converts the current millisecond time value time to calendar field values in fields[]. |
| 10 | protected abstract void computeTime() | This method converts the current calendar field values in fields[] to the millisecond time value time. |
| 11 | boolean equals(Object obj) | This method compares this Calendar to the specified Object. |
| 12 | int get(int field) | This method returns the value of the given calendar field. |
| 13 | int getActualMaximum(int field) | This method returns the maximum value that the specified calendar field could have, given the time value of the Calendar. |
| 14 | int getActualMinimum(int field) | This method returns the minimum value that the specified calendar field could have, given the time value of this Calendar. |
| 15 | static Locale[] getAvailableLocales() | This method returns an array of all locales for which the getInstance methods of this class can return localized instances |
| 16 | String getDisplayName(int field, int style, Locale locale) | This method returns the string representation of the calendar field value in the given style and locale. |
| 17 | Map<String,Integer> getDisplayNames(int field, int style, Locale locale) | This method returns a Map containing all names of the calendar field in the given style and locale and their corresponding field values |
| 18 | int getFirstDayOfWeek() | This method gets what the first day of the week is; e.g., SUNDAY in the U.S., MONDAY in France. |
| 19 | abstract int getGreatestMinimum(int field) | This method returns the highest minimum value for the given calendar field of this Calendar instance. |
| 20 | static Calendar getInstance() | This method gets a calendar using the default time zone and locale. |
| 21 | static Calendar getInstance(Locale aLocale) | This method gets a calendar using the default time zone and specified locale. |
| 22 | static Calendar getInstance(TimeZone zone) | This method gets a calendar using the specified time zone and default locale. |
| 23 | static Calendar getInstance(TimeZone zone, Locale aLocale) | This method gets a calendar with the specified time zone and locale. |
| 24 | abstract int getLeastMaximum(int field) | This method returns the lowest maximum value for the given calendar field of this Calendar instance. |
| 25 | abstract int getMaximum(int field) | This method returns the maximum value for the given calendar field of this Calendar instance. |
| 26 | int getMinimalDaysInFirstWeek() | This method gets what the minimal days required in the first week of the year are; e.g., if the first week is defined as one that contains the first day of the first month of a year, this method returns 1. |
| 27 | abstract int getMinimum(int field) | This method returns the minimum value for the given calendar field of this Calendar instance. |
| 28 | Date getTime() | This method returns a Date as an object representing this Calendar’s time value |
| 29 | long getTimeInMillis() | This method returns this Calendar’s time value in milliseconds. |
| 30 | TimeZone getTimeZone() | This method gets the time zone. |
| 31 | int getWeeksInWeekYear() | This method returns the number of weeks in the week year represented by this Calendar. |
| 32 | int getWeekYear() | This method returns the week year represented by this Calendar. |
| 33 | int hashCode() | This method returns a hash code for this calendar. |
| 34 | protected int internalGet(int field) | This method returns the value of the given calendar field. |
| 35 | boolean isLenient() | This method tells whether date/time interpretation is to be lenient. |
| 36 | boolean isSet(int field) | This method determines if the given calendar field has a value set, including cases where the value has been set by internal fields calculations triggered by a get method call. |
| 37 | abstract void roll(int field, boolean up) | This method adds or subtracts a single unit of time on the given time field without changing larger fields. |
| 38 | void roll(int field, int amount) | This method adds the specified amount to the specified calendar field without changing larger fields. |
| 39 | void set(int field, int value) | This method sets the given calendar field to the given value. |
| 40 | void set(int year, int month, int date) | This method sets the values for the calendar fields YEAR, MONTH, and DAY_OF_MONTH. |
| 41 | void set(int year, int month, int date, int hourOfDay, int minute) | This method sets the values for the calendar fields YEAR, MONTH, DAY_OF_MONTH, HOUR_OF_DAY, and MINUTE. |
| 42 | void set(int year, int month, int date, int hourOfDay, int minute, int second) | This method sets the values for the fields YEAR, MONTH, DAY_OF_MONTH, HOUR, MINUTE, and SECOND. |
| 43 | void setFirstDayOfWeek(int value) | This method sets what the first day of the week is; e.g., SUNDAY in the U.S., MONDAY in France. |
| 44 | void setLenient(boolean lenient) | This method specifies whether or not date/time interpretation is to be lenient. |
| 45 | void setMinimalDaysInFirstWeek(int value) | This method sets what the minimum days required in the first week of the year are; For example, if the first week is defined as one that contains the first day of the first month of a year, call this method with the value 1. |
| 46 | void setTime(Date date) | This method sets this Calendar’s time with the given Date. |
| 47 | void setTimeInMillis(long millis) | This method sets this Calendar’s current time from the given long value. |
| 48 | void setTimeZone(TimeZone value) | This method sets the time zone with the given time zone value. |
| 49 | void setWeekDate(int weekYear, int weekOfYear, int dayOfWeek) | This method sets the date of this Calendar with the given date specifiers – week year, week of the year, and day of the week. |
| 50 | String toString() | This method returns a string representation of this calendar. |
Java Program to get date and time
To get the current date and time we can use the getTime() method. Let’s see an example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Calendar object
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// To get the current date and time
System.out.print("Current Date and Time is - " + calendar.getTime());
}
} Output:

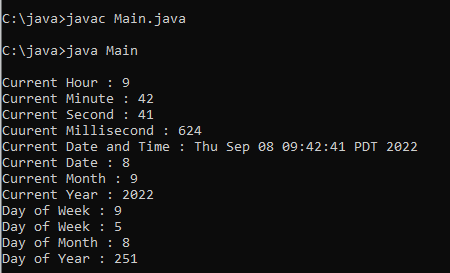
To get information about the current date, and time details separately we can use the following way.
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating Calendar object
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
// To get hour of the current day
int hours = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR);
// To get minute of the current day
int minutes = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
// To get hour of the current day
int seconds = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND);
// To get hour of the current day
int milliseconds = calendar.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);
// To get hour of the current day
int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DATE);
// To get hour of the current day
int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1;
// To get hour of the current day
int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
// To get hour of the current day
int dayOfWeek = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
// To get hour of the current day
int dayOfMonth = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
// To get hour of the current day
int dayOfYear = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR);
// To get hour of the current day
int hourOfDay = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
System.out.println("\nCurrent Hour : " + hours);
System.out.println("Current Minute : " + minutes);
System.out.println("Current Second : " + seconds);
System.out.println("Cuurent Millisecond : " + milliseconds);
System.out.println("Current Date and Time : " + calendar.getTime());
System.out.println("Current Date : " + day);
System.out.println("Current Month : " + month);
System.out.println("Current Year : " + year);
System.out.println("Day of Week : " + hourOfDay);
System.out.println("Day of Week : " + dayOfWeek);
System.out.println("Day of Month : " + dayOfMonth);
System.out.println("Day of Year : " + dayOfYear);
}
}Output:
If we want to get the previous or following month, year or date we can use the following way.
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
//To get the date and time 25 days ago from the current date
calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, -25);
System.out.println("25 days ago: " + calendar.getTime());
//To get the date and time 2 months later from the current date
calendar.add(Calendar.MONTH, 2);
System.out.println("2 months later: " + calendar.getTime());
//To get the date and time 5 years later from the current date
calendar.add(Calendar.YEAR, 5);
System.out.println("5 years later: " + calendar.getTime());
}
} Output:

Java Program to print the Calendar of any month
We are going to write a Java program to print the Calendar for any month. The program prompts the user to enter the year and the month and then prints the calendar for the month of the year. We can solve the problem in many ways, as long as we get the same output.
The program does validate user input. For instance, if the user enters either a month or not in the range between 1 and 12, the program would display an error. To avoid this error, add an if statement to check the input before printing the calendar.
Some of the important points to be noted for writing the program are as follows.
1) January, March, May, July, August, October, and December have thirty-one days.
2) April, June, September, and November have thirty days.
3) February has twenty-eight days during a normal year and twenty-nine days during a leap year. A regular year, therefore, has 365 days, and a leap year has 366 days.
#Importing the library
import java.util*;
public class MonthCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.print("Enter year : ");
int year = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter month : ");
int month = scan.nextInt();
if (month < 1 || month > 12)
System.out.println("Wrong input!");
else
printMonth(year, month);
}
static void printMonth(int year, int month) {
printMonthTitle(year, month);
printMonthBody(year, month);
}
static void printMonthTitle(int year, int month) {
System.out.println(" " + getMonthName(month) + " " + year);
System.out.println(" Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat");
}
static String getMonthName(int month) {
String monthName = null;
switch (month) {
case 1: monthName = "January"; break;
case 2: monthName = "February"; break;
case 3: monthName = "March"; break;
case 4: monthName = "April"; break;
case 5: monthName = "May"; break;
case 6: monthName = "June"; break;
case 7: monthName = "July"; break;
case 8: monthName = "August"; break;
case 9: monthName = "September"; break;
case 10: monthName = "October"; break;
case 11: monthName = "November"; break;
case 12: monthName = "December";
}
return monthName;
}
static void printMonthBody(int year, int month) {
int startDay = getStartDay(year, month);
int numberOfDaysInMonth = getNumberOfDaysInMonth(year, month);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < startDay; i++)
System.out.print(" ");
for (i = 1; i <= numberOfDaysInMonth; i++) {
if (i < 10)
System.out.print(" " + i);
else
System.out.print(" " + i);
if ((i + startDay) % 7 == 0)
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
static int getStartDay(int year, int month) {
int startDay1800 = 3;
int totalNumberOfDays = getTotalNumberOfDays(year, month);
return (totalNumberOfDays + startDay1800) % 7;
}
static int getTotalNumberOfDays(int year, int month) {
int total = 0;
for (int i = 1800; i < year; i++)
if (isLeapYear(i))
total = total + 366;
else
total = total + 365;
for (int i = 1; i < month; i++)
total = total + getNumberOfDaysInMonth(year, i);
return total;
}
static int getNumberOfDaysInMonth(int year, int month) {
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12)
return 31;
if (month == 4 || month == 6 || month == 9 || month == 11)
return 30;
if (month == 2) return isLeapYear(year) ? 29 : 28;
return 0;
}
static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
return year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0);
}
}
Output:

Java Program to print the Calendar of any month without using inbuilt Calendar methods
We are going to write a Java program to print the Calendar for any month. The program prompts the user to enter the year and the month and then prints the calendar for the month of the year. We can solve the problem in many ways, as long as we get the same output.
First, let us take the year and the month as inputs from the user. Then, create two arrays for storing days and months, as per proper order. Initialize a counter variable and three variables, each for the day, month, and year as 1, and a separate array for storing the different combinations of days on which months can be found.
Then, check the leap year condition for the input month and re-initialize values for the above array. Increment year count as month count reaches 12 and increment month count as day count reaches a value greater than that present in the array for the respective index. Finally print the calendar.
#Importing the libraries
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class MonthCalendar {
public static void main(String a[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the year : ");
int yy = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter month : ");
int mm = sc.nextInt();
int d = 1;
int month = 1;
int year = 1;
int day = 1;
// Storing the name of days
String days[] = { "SUN", "MON", "TUE", "WED", "THU", "FRI", "SAT" };
// Storing the name of months
String months[]
= { "JANUARY", "FEBRUARY", "MARCH","APRIL", "MAY", "JUNE",
"JULY", "AUGUST", "SEPTEMBER","OCTOBER", "NOVEMBER", "DECEMBER" };
// Storing the number of days in each month
int ar[] = { 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30,31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
while (true) {
if (d == 1 && month == mm && year == yy) {
break;
}
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 100 == 0) {
ar[1] = 29;
}
else {
ar[1] = 28;
}
day++;d++;
if (d > ar[month - 1]) {
month++;
d = 1;
}
if (month > 12) {
month = 1;year++;
}
if (day == 7) {
day = 0;
}
}
int c = day;
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0) {
ar[1] = 29;
}
else {
ar[1] = 28;
}
System.out.println("MONTH:" + months[mm - 1]);
for (int k = 0; k < 7; k++) {
System.out.print(" " + days[k]);
}
System.out.println();
for (int j = 1; j <= (ar[mm - 1] + day); j++) {
if (j > 6) {
day = day % 6;
}
}
int spaces = day;
if (spaces < 0)
spaces = 6;
# Printing the Calendar
for (int i = 0; i < spaces; i++)
System.out.print(" ");
for (int i = 1; i <= ar[mm - 1]; i++) {
System.out.printf(" %2d ", i);
if (((i + spaces) % 7 == 0)
|| (i == ar[mm - 1]))
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output:

Conclusion
In this article, we have learned to code Calender using Java. We have also discussed the Calender class and methods in Java. We also discussed how to print calendar of any Month without the use of the Calendar class. Hope you enjoyed learning and coding with us!
Also Read:
- Download 1000+ Projects, All B.Tech & Programming Notes, Job, Resume & Interview Guide, and More – Get Your Ultimate Programming Bundle!
- Music Recommendation System in Machine Learning
- Dino Game in Java
- Java Games Code | Copy And Paste
- Supply Chain Management System in Java
- Survey Management System In Java
- Phone Book in Java
- Email Application in Java
- Inventory Management System Project in Java
- Blood Bank Management System Project in Java
- Electricity Bill Management System Project in Java
- CGPA Calculator App In Java
- Chat Application in Java
- CRUD Operations in Servlet & JSP
- 100+ Java Projects for Beginners 2023
- Airline Reservation System Project in Java
- Password and Notes Manager in Java
- GUI Number Guessing Game in Java
- How to create Notepad in Java?
- Memory Game in Java
- Simple Car Race Game in Java
- ATM program in Java
- Drawing Application In Java
- Tetris Game in Java
- Pong Game in Java
- Hospital Management System Project in Java
- Ludo Game in Java
- Restaurant Management System Project in Java
- Flappy Bird Game in Java
- HackerRank Day 8 Solution in Python: Dictionaries and Maps