Today, we will be creating a GUI application of spell checker in Python. We will use two famous libraries in Python that can be used to check the spelling of a word and can also suggest the correct word that should be used in place of that wrong word. Two libraries are pyspellchecker and Textblob.
1. pyspellchecker
pyspellchecker is based on Peter Norvig’s blog post on setting up a simple spell-checking algorithm. You can google it if you want to understand it in depth.
In short, it uses a Levenshtein Distance algorithm to find permutations within an edit distance of 2 from the original word and then compares all permutations to known words in a word frequency list. The more frequent words are the more likely the correct results.
It can be used to check the spelling of the following languages English, Spanish, German, French, and Portuguese.
Use the command below to install pyspellchecker:
pip install pyspellchecker
Code for Spell checker in Python using pyspellchecker
# Importing tkinter module
from spellchecker import SpellChecker
from tkinter import *
# Initializing tkinter here
root = Tk()
root.geometry("400x300") # width and height of GUI
root.title(" Spelling Checker ")
# Using pyspellchecker library
class Spell:
# Constructor that will be called from main.py with word entered by user as its parameter
def __init__(self, text):
self.text = text
# Object creation for SpellChecker class
self.spell = SpellChecker()
# This method returns a formatted string of all likely correct spelling of the word entered by user
def correctSpelling(self):
# correction() takes the word as parameter and returns it's most likely correct spelling
correct = self.spell.correction(self.text)
# candidates() takes the word as parameter and returns a list of all likely correct spellings of the word
candidates = self.spell.candidates(self.text)
for i in candidates:
if (i != correct):
correct = correct+'\n'+i
return correct
# Returns True, if spelling is correct else False
def check(self):
# the method unknown() takes a list of words as parameter and returns the list of misspelled words
# So, if spelling is correct, it returns an empty list
misspelled = self.spell.unknown([self.text])
for i in misspelled:
print(i)
if (len(misspelled) == 0):
return True
else:
return False
# This method will get triggered when the Check button (Initialized below) gets clicked
def takeInput():
# This method, first clears the output screen, in case any text is already present on output screen
Output.delete("1.0", "end")
# Then store the text entered on input screen in Input variable.
Input = inputText.get("1.0", "end-1c")
# As of now, it is programmed for only single word at once.
# So, if user enters multiple words we are considering the first word
Input = Input.split()[0]
# Creating an object of type Spell, more explanation about this class is present in another files.
# We can refer to spell1.py and spell2.py files respectively, depending on which one we have imported
s = Spell(Input)
# This method takes Input as parameter and return True if spelling is correct else false
if (s.check()):
Output.insert(END, 'Correct!')
else:
# In case spelling is incorrect, the below method returns the likely correct spellings in the form of formatted string
correctSpellings = s.correctSpelling()
Output.insert(
END, 'Incorrect!, Do you mean any of these: '+correctSpellings)
# Label is a widget provided by tkinter to display text/image on screen, it can take different parameters as you can see below.
# Try changing few and see how the GUI changes
l = Label(text="Type the word here: ", bg='#759D98',
bd='4', font=("Times", "23", "bold"), width='40')
# Here, Text widget is initialized and assigned to the variable inputText.
# inputText is being used above, to take the word entered by user, store it in a variable and pass on to methods to check its spelling
inputText = Text(root, height=2,
width=40, bd='3', font=("Times", "18", "bold"))
# The button widget is initialized here, this will add a button with name Check, on cliking which the method takeInput will get triggered
Check = Button(root, height=2,
width=20,
text="Check",
command=lambda: takeInput(), bg='#375F5A', fg='white', font=("Times", "14"))
# Here, the text box is initialized, where the final result after checking spelling will be displayed
Output = Text(root, height=5,
width=40, bd='3', bg='#8C9F9D', font=("Times", "18", "bold"))
# the pack() method declares the position of widgets in relation to each other, instead of declaring the precise location of a widget
l.pack(padx=2, pady=2)
inputText.pack(padx=5, pady=5)
Check.pack(padx=2, pady=2)
Output.pack(pady=5)
# This is to call an endless loop so that the GUI window stays open until the user closes it
mainloop()2. Textblob
Textblob is mainly used for common natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as part-of-speech tagging, noun phrase extraction, sentiment analysis, classification, translation, etc.
But it also provides methods for checking to spell and getting the list of likely correct spellings of misspelled words.
Use the command below to install Textblob:
pip install textblob
Code for Spell checker in Python using Textblob
from textblob import Word
from tkinter import *
# Initializing tkinter here
root = Tk()
root.geometry("400x300") # width and height of GUI
root.title(" Spelling Checker ")
# Using textblob
# This class will be imported in main.py if we import from spell1.py
class Spell:
# contructor, In main.py, while object creation we'll pass the word entered by user as parameter
def __init__(self, text):
self.word = Word(text)
# This method is getting list of likely correct spellings of the word using method provided by textblob and returning it as a string
def correctSpelling(self):
# returns list of likely correct spellings of the word
tempList = self.word.spellcheck()
temp = ''
for i in tempList:
temp = temp+i[0]+'\n'
return temp
# The method spellcheck provided with textblob returns a list of likely correct spellings of the word, along with their accuracy
# If the spelling is correct, then it returns the same word with accuracy as 1
# This check method is using the spellcheck method and returning true if spelling of word entered is correct, else false
def check(self):
correct = self.word.spellcheck()[0][0]
if (self.word == correct):
return True
else:
return False
# This method will get triggered when the Check button (Initialized below) gets clicked
def takeInput():
# This method, first clears the output screen, in case any text is already present on output screen
Output.delete("1.0", "end")
# Then store the text entered on input screen in Input variable.
Input = inputText.get("1.0", "end-1c")
# As of now, it is programmed for only single word at once.
# So, if user enters multiple words we are considering the first word
Input = Input.split()[0]
# Creating an object of type Spell, more explanation about this class is present in another files.
# We can refer to spell1.py and spell2.py files respectively, depending on which one we have imported
s = Spell(Input)
# This method takes Input as parameter and return True if spelling is correct else false
if (s.check()):
Output.insert(END, 'Correct!')
else:
# In case spelling is incorrect, the below method returns the likely correct spellings in the form of formatted string
correctSpellings = s.correctSpelling()
Output.insert(
END, 'Incorrect!, Do you mean any of these: '+correctSpellings)
# Label is a widget provided by tkinter to display text/image on screen, it can take different parameters as you can see below.
# Try changing few and see how the GUI changes
l = Label(text="Type the word here: ", bg='#759D98',
bd='4', font=("Times", "23", "bold"), width='40')
# Here, Text widget is initialized and assigned to the variable inputText.
# inputText is being used above, to take the word entered by user, store it in a variable and pass on to methods to check its spelling
inputText = Text(root, height=2,
width=40, bd='3', font=("Times", "18", "bold"))
# The button widget is initialized here, this will add a button with name Check, on cliking which the method takeInput will get triggered
Check = Button(root, height=2,
width=20,
text="Check",
command=lambda: takeInput(), bg='#375F5A', fg='white', font=("Times", "14"))
# Here, the text box is initialized, where the final result after checking spelling will be displayed
Output = Text(root, height=5,
width=40, bd='3', bg='#8C9F9D', font=("Times", "18", "bold"))
# the pack() method declares the position of widgets in relation to each other, instead of declaring the precise location of a widget
l.pack(padx=2, pady=2)
inputText.pack(padx=5, pady=5)
Check.pack(padx=2, pady=2)
Output.pack(pady=5)
# This is to call an endless loop so that the GUI window stays open until the user closes it
mainloop()Output for Spell Checker in Python:
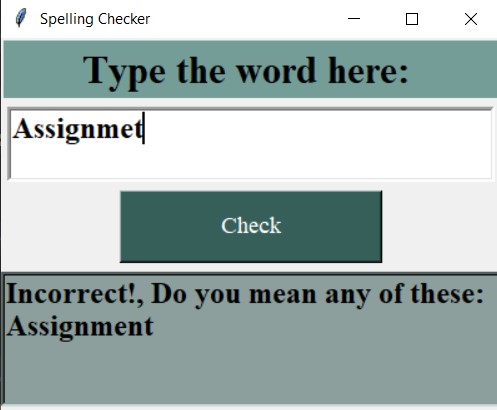
Image output:

Video output:
Conclusion
So, we created a GUI application of Spell Checker in Python from scratch. We have used 2 different libraries to create this spell checker. You can use this app to check and correct your spelling. This app works much like Grammarly as we all know is a tool used mostly to check to spell while doing any writing work. Hope you enjoyed this article.
Thank you for visiting our website.
Also Read:
- Create your own ChatGPT with Python
- SQLite | CRUD Operations in Python
- Event Management System Project in Python
- Ticket Booking and Management in Python
- Hostel Management System Project in Python
- Sales Management System Project in Python
- Bank Management System Project in C++
- Python Download File from URL | 4 Methods
- Python Programming Examples | Fundamental Programs in Python
- Spell Checker in Python
- Portfolio Management System in Python
- Stickman Game in Python
- Contact Book project in Python
- Loan Management System Project in Python
- Cab Booking System in Python
- Brick Breaker Game in Python
- Tank game in Python
- GUI Piano in Python
- Ludo Game in Python
- Rock Paper Scissors Game in Python
- Snake and Ladder Game in Python
- Puzzle Game in Python
- Medical Store Management System Project in Python
- Creating Dino Game in Python
- Tic Tac Toe Game in Python
- Test Typing Speed using Python App
- Scientific Calculator in Python
- GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter
- Scientific Calculator in Python using Tkinter
- GUI Chat Application in Python Tkinter



