Introduction
Hello friends, today we will create GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter. Python tkinter is a standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit. The design of this system is rather straightforward, so the user will encounter no issues when working on it.
We will be using the tkinter library for GUI and SQLite for the database. After the 2.5 version of Python, both libraries are builtin with python.
GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter: Project Overview
| Project Name: | GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter |
| Abstract | It’s a GUI-based project used with the tkinter module to organize all the elements that work under the to-do list app in python. |
| Language/s Used: | Python |
| IDE | PyCharm and Thonny(recommended for beginners) |
| Python version (Recommended): | Python 3.x |
| Database: | SQLite |
| Type: | Desktop Application |
| Recommended for | Beginner and intermediate Python programmers |
Complete code to create GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter:
# importing the required modules
from tkinter import *
# importing the messagebox module from the tkinter library
from tkinter import messagebox
# importing the sqlite3 module as sql
import sqlite3 as sql
# defining the function to add tasks to the list
def add_task():
# getting the string from the entry field
task_string = task_field.get()
# checking whether the string is empty or not
if len(task_string) == 0:
# displaying a message box with 'Empty Field' message
messagebox.showinfo('Error', 'Field is Empty.')
else:
# adding the string to the tasks list
tasks.append(task_string)
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('insert into tasks values (?)', (task_string ,))
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# deleting the entry in the entry field
task_field.delete(0, 'end')
# defining the function to update the list
def list_update():
# calling the function to clear the list
clear_list()
# iterating through the strings in the list
for task in tasks:
# using the insert() method to insert the tasks in the list box
task_listbox.insert('end', task)
# defining the function to delete a task from the list
def delete_task():
# using the try-except method
try:
# getting the selected entry from the list box
the_value = task_listbox.get(task_listbox.curselection())
# checking if the stored value is present in the tasks list
if the_value in tasks:
# removing the task from the list
tasks.remove(the_value)
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('delete from tasks where title = ?', (the_value,))
except:
# displaying the message box with 'No Item Selected' message for an exception
messagebox.showinfo('Error', 'No Task Selected. Cannot Delete.')
# function to delete all tasks from the list
def delete_all_tasks():
# displaying a message box to ask user for confirmation
message_box = messagebox.askyesno('Delete All', 'Are you sure?')
# if the value turns to be True
if message_box == True:
# using while loop to iterate through the tasks list until it's empty
while(len(tasks) != 0):
# using the pop() method to pop out the elements from the list
tasks.pop()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('delete from tasks')
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# function to clear the list
def clear_list():
# using the delete method to delete all entries from the list box
task_listbox.delete(0, 'end')
# function to close the application
def close():
# printing the elements from the tasks list
print(tasks)
# using the destroy() method to close the application
guiWindow.destroy()
# function to retrieve data from the database
def retrieve_database():
# using the while loop to iterate through the elements in the tasks list
while(len(tasks) != 0):
# using the pop() method to pop out the elements from the list
tasks.pop()
# iterating through the rows in the database table
for row in the_cursor.execute('select title from tasks'):
# using the append() method to insert the titles from the table in the list
tasks.append(row[0])
# main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# creating an object of the Tk() class
guiWindow = Tk()
# setting the title of the window
guiWindow.title("To-Do List ")
# setting the geometry of the window
guiWindow.geometry("665x400+550+250")
# disabling the resizable option
guiWindow.resizable(0, 0)
# setting the background color to #B5E5CF
guiWindow.configure(bg = "#B5E5CF")
# using the connect() method to connect to the database
the_connection = sql.connect('listOfTasks.db')
# creating the cursor object of the cursor class
the_cursor = the_connection.cursor()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('create table if not exists tasks (title text)')
# defining an empty list
tasks = []
# defining frames using the tk.Frame() widget
functions_frame = Frame(guiWindow, bg = "black")
# using the pack() method to place the frames in the application
functions_frame.pack(side = "top", expand = True, fill = "both")
# defining another label using the Label() widget
task_label = Label( functions_frame,text = "Enter the Task:",
font = ("arial", "14", "bold"),
background = "black",
foreground="white"
)
# using the place() method to place the label in the application
task_label.place(x = 20, y = 30)
# defining an entry field using the Entry() widget
task_field = Entry(
functions_frame,
font = ("Arial", "14"),
width = 42,
foreground="black",
background = "white",
)
# using the place() method to place the entry field in the application
task_field.place(x = 180, y = 30)
# adding buttons to the application using the Button() widget
add_button =Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Add Task",
width = 15,
bg='#D4AC0D',font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = add_task,
)
del_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Delete Task",
width = 15,
bg='#D4AC0D', font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = delete_task,
)
del_all_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Delete All Tasks",
width = 15,
font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
bg='#D4AC0D',
command = delete_all_tasks
)
exit_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Exit",
width = 52,
bg='#D4AC0D', font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = close
)
# using the place() method to set the position of the buttons in the application
add_button.place(x = 18, y = 80,)
del_button.place(x = 240, y = 80)
del_all_button.place(x = 460, y = 80)
exit_button.place(x = 17, y = 330)
# defining a list box using the tk.Listbox() widget
task_listbox = Listbox(
functions_frame,
width = 57,
height = 7,
font="bold",
selectmode = 'SINGLE',
background = "WHITE",
foreground="BLACK",
selectbackground = "#D4AC0D",
selectforeground="BLACK"
)
# using the place() method to place the list box in the application
task_listbox.place(x = 17, y = 140)
# calling some functions
retrieve_database()
list_update()
# using the mainloop() method to run the application
guiWindow.mainloop()
# establishing the connection with database
the_connection.commit()
the_cursor.close()Now, let’s understand our GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter step by step by breaking code into sub-parts.
Step.1: Import libraries for To-Do List App
# importing the required modules from tkinter import * # importing the messagebox module from the tkinter library from tkinter import messagebox # importing the sqlite3 module as sql import sqlite3 as sql
In the above code, we imported the tkinter module as tk. The Tkinter messagebox was then imported. Finally, the sqlite3 module was loaded as sql.
Step.2: Creating function for buttons:
# defining the function to add tasks to the list
def add_task():
# getting the string from the entry field
task_string = task_field.get()
# checking whether the string is empty or not
if len(task_string) == 0:
# displaying a message box with 'Empty Field' message
messagebox.showinfo('Error', 'Field is Empty.')
else:
# adding the string to the tasks list
tasks.append(task_string)
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('insert into tasks values (?)', (task_string ,))
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# deleting the entry in the entry field
task_field.delete(0, 'end')The above code determines if the string is inserted or not and stores it in the database of the To-Do List App.
# defining the function to update the list
def list_update():
# calling the function to clear the list
clear_list()
# iterating through the strings in the list
for task in tasks:
# using the insert() method to insert the tasks in the list box
task_listbox.insert('end', task)
# defining the function to delete a task from the list
def delete_task():
# using the try-except method
try:
# getting the selected entry from the list box
the_value = task_listbox.get(task_listbox.curselection())
# checking if the stored value is present in the tasks list
if the_value in tasks:
# removing the task from the list
tasks.remove(the_value)
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('delete from tasks where title = ?', (the_value,))
except:
# displaying the message box with 'No Item Selected' message for an exception
messagebox.showinfo('Error', 'No Task Selected. Cannot Delete.')
# function to delete all tasks from the list
def delete_all_tasks():
# displaying a message box to ask user for confirmation
message_box = messagebox.askyesno('Delete All', 'Are you sure?')
# if the value turns to be True
if message_box == True:
# using while loop to iterate through the tasks list until it's empty
while(len(tasks) != 0):
# using the pop() method to pop out the elements from the list
tasks.pop()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('delete from tasks')
# calling the function to update the list
list_update()
# function to clear the list
def clear_list():
# using the delete method to delete all entries from the list box
task_listbox.delete(0, 'end')
# function to close the application
def close():
# printing the elements from the tasks list
print(tasks)
# using the destroy() method to close the application
guiWindow.destroy()
# function to retrieve data from the database
def retrieve_database():
# using the while loop to iterate through the elements in the tasks list
while(len(tasks) != 0):
# using the pop() method to pop out the elements from the list
tasks.pop()
# iterating through the rows in the database table
for row in the_cursor.execute('select title from tasks'):
# using the append() method to insert the titles from the table in the list
tasks.append(row[0])Step.3: Creating GUI of To-Do List App
# main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# creating an object of the Tk() class
guiWindow = Tk()
# setting the title of the window
guiWindow.title("To-Do List ")
# setting the geometry of the window
guiWindow.geometry("665x400+550+250")
# disabling the resizable option
guiWindow.resizable(0, 0)
# setting the background color to #B5E5CF
guiWindow.configure(bg = "#B5E5CF")
# using the connect() method to connect to the database
the_connection = sql.connect('listOfTasks.db')
# creating the cursor object of the cursor class
the_cursor = the_connection.cursor()
# using the execute() method to execute a SQL statement
the_cursor.execute('create table if not exists tasks (title text)')
# defining an empty list
tasks = []
# defining frames using the tk.Frame() widget
functions_frame = Frame(guiWindow, bg = "black")
# using the pack() method to place the frames in the application
functions_frame.pack(side = "top", expand = True, fill = "both")Step.4: Create a task entry widget and design the button
# defining another label using the Label() widget
task_label = Label( functions_frame,text = "Enter the Task:",
font = ("arial", "14", "bold"),
background = "black",
foreground="white"
)
# using the place() method to place the label in the application
task_label.place(x = 20, y = 30)
# defining an entry field using the Entry() widget
task_field = Entry(
functions_frame,
font = ("Arial", "14"),
width = 42,
foreground="black",
background = "white",
)
# using the place() method to place the entry field in the application
task_field.place(x = 180, y = 30)
# adding buttons to the application using the Button() widget
add_button =Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Add Task",
width = 15,
bg='#D4AC0D',font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = add_task,
)
del_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Delete Task",
width = 15,
bg='#D4AC0D', font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = delete_task,
)
del_all_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Delete All Tasks",
width = 15,
font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
bg='#D4AC0D',
command = delete_all_tasks
)
exit_button = Button(
functions_frame,
text = "Exit",
width = 52,
bg='#D4AC0D', font=("arial", "14", "bold"),
command = close
)
# using the place() method to set the position of the buttons in the application
add_button.place(x = 18, y = 80,)
del_button.place(x = 240, y = 80)
del_all_button.place(x = 460, y = 80)
exit_button.place(x = 17, y = 330)Step.5: Creating list box layout and updating the database
# defining a list box using the tk.Listbox() widget
task_listbox = Listbox(
functions_frame,
width = 57,
height = 7,
font="bold",
selectmode = 'SINGLE',
background = "WHITE",
foreground="BLACK",
selectbackground = "#D4AC0D",
selectforeground="BLACK"
)
# using the place() method to place the list box in the application
task_listbox.place(x = 17, y = 140)
# calling some functions
retrieve_database()
list_update()
# using the mainloop() method to run the application
guiWindow.mainloop()
# establishing the connection with database
the_connection.commit()
the_cursor.close()The Listbox widget is used to show the user the list of items. The location of the listbox is also specified. Python calls window.mainloop() to start the Tkinter event loop for To-Do List App.
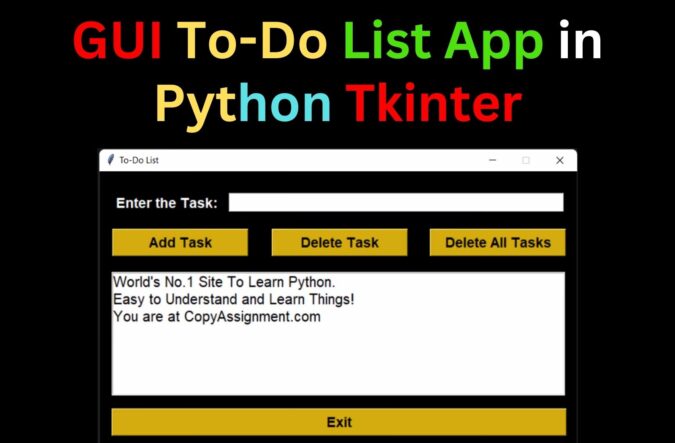
Output for GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter:
We successfully created the GUI To-Do List App in Python Tkinter. This project is suitable for students who wish to learn Python programming since it has a Graphical User Interface (GUI) and a user-friendly interface. This project on To-Do List App is easy to understand and run, and it is exclusively for educational purposes.
Also Read:
- Brick Breaker Game in C++
- Create your own ChatGPT with Python
- Bakery Management System in Python | Class 12 Project
- SQLite | CRUD Operations in Python
- Event Management System Project in Python
- Ticket Booking and Management in Python
- Hostel Management System Project in Python
- Sales Management System Project in Python
- Bank Management System Project in C++
- Python Download File from URL | 4 Methods
- Python Programming Examples | Fundamental Programs in Python
- Spell Checker in Python
- Portfolio Management System in Python
- Stickman Game in Python
- Contact Book project in Python
- Loan Management System Project in Python
- Cab Booking System in Python
- Brick Breaker Game in Python
- 100+ Java Projects for Beginners 2023
- Tank game in Python
- GUI Piano in Python
- Best JavaScript Projects for Beginners in 2023
- Ludo Game in Python
- Rock Paper Scissors Game in Python
- Snake and Ladder Game in Python
- Puzzle Game in Python
- Medical Store Management System Project in Python
- Creating Dino Game in Python
- Tic Tac Toe Game in Python
- Best Java Roadmap for Beginners 2023



