In this article, we will explore the 3 V’s of Big data. Big data is one of the most trending topics in the last two decades. It is due to the massive amount of data that has been produced as well as consumed by everyone across the globe. Major evolution in the internet during the past years led to this drastic amount of data generation. Have you ever realized that even you are a tiny part of this massive big data? Exciting right? Let’s jump into the article to discuss more Big data and its 3 V’s of Big data.
What is Big data?
We know that Big data refers to large sets of raw data, and that data can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. We cannot specify a single source from which data is originating, it is collected from a variety of sources, ranging from business transactions, photographs, videos, search engines, social media, websites, apps, and much more. This information is gathered, recorded, stored, and analyzed with the purpose of getting meaningful insights that will help the organization grow.
Big Data is much more than simply lots of data. It is a way of providing opportunities to utilize new and existing data, and discovering fresh ways of capturing future data to really make a difference to business operatives and make it more agile. With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), more objects and devices are connected to the internet, gathering data on customer usage patterns and product performance. The emergence of machine learning has produced still more data.
The 3 V’s of Big data
The 3 V’s of Big data contains 3 main characteristics of Big Data. These characteristics are Volume, Velocity, and Variety. Each keyword is self-explanatory and its characteristics demonstrate physical as well as logical attributes. The 3 V’s of Big data are also defined as the three defining properties or dimensions of big data. Volume refers to the amount of data, variety refers to the number of types of data and velocity refers to the speed of data processing.
According to the 3 V’s of the Big data model, the challenges of big data management result from the expansion of all three properties, rather than just the volume alone. So all three properties of Big data are equally important. An organization can be better equipped to deal with big data challenges by understanding the 3 V’s of Big data management.
Volume
From the word we can understand that volume In Big data means a huge set of data that has a huge form. The volume describes the massive amount of data which is very complex to process to extract valuable information from it. Within the Social Media space, for example, Volume refers to the amount of data generated through websites, portals, and online applications. Especially for B2C companies, Volume encompasses the available data that are out there and need to be assessed for relevance.
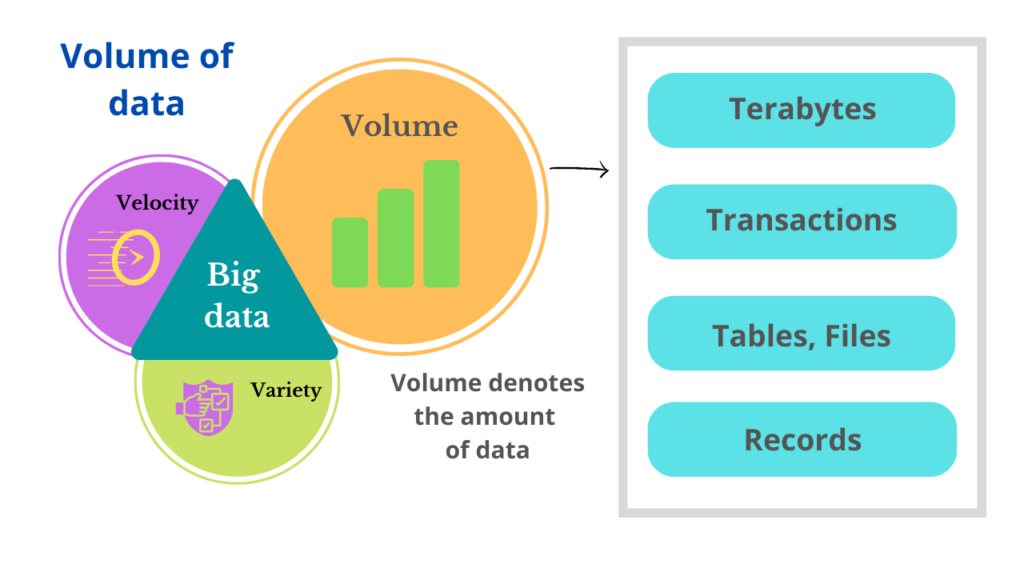
The size of Bigdata could be in large notations such as Terabyte, Exabyte, or even Zettabyte. The size of big data makes it very complex to process. For Example, Facebook stores more than 250 billion images in total. It increases every day as people keep on posting on the platform.
Velocity
In big data, Velocity denotes two things mainly, the Speed of growth of data and the Speed of transmission of data. Velocity refers to data generating, increasing, and sharing at a particular speed through the resources. The data increases day by day through various resources.
As you see, users on social media and the content increasing every day, so they are generating a huge bunch of data. IoT is also superior technology for contributing to big data. Apart from the amount of data, the Speed of data generated also takes a major role in identifying big data. Data increases in a rapid manner which makes it very complex to process fast and makes it difficult to transmit quickly.

Big Data helps the company to hold the data explosion, it accepts the incoming flow of data and at the same time process it fast so that it does not create bottlenecks. For Example, Twitter generates more than 500 Million tweets per day, rate of speed of generation of data and rate of speed of transmission of data is very high.
Variety
In big data, Variety is nothing but different forms of data. We know that traditional data types were structured and fit neatly in a relational database. With the rise of big data, data comes in new unstructured data types. This means various types of data such as texts, audio, videos, XML file, data in rows and columns, etc. are generated.

Each type of data have a separate way to process itself therefore, it is necessary to categorize different types of data, before analyzing them. Big data is all about the ability to classify incoming data into various categories.
For example, Instagram generates a variety of data formats such as photos, videos, and texts.
How does Big data work?
The development of open-source frameworks, such as Hadoop and Spark was essential for the growth of big data because they make it easier to work with and cheaper to store. In the years since then, the volume of data has increased massively. Hadoop and Spark usage has significant cost advantages for storing, processing, and analyzing large volumes of data.
While big data has come far, its usefulness is only just beginning. Cloud computing has expanded big data possibilities even further. The cloud offers truly elastic scalability for handling data and graph databases have the ability to display massive amounts of data in a way that makes analytics fast and comprehensive.
Following is the four steps or process held in big data:
1. Collection
As we know, Big data brings together data from many sources and applications. Traditional data integration mechanisms, such as extract, transform, and load (ETL) generally are not up to the task. It requires new strategies and technologies to analyze big data sets at terabytes or even more scale. During integration, we need to bring in the data, process it, and make sure it’s formatted.
2. Storage
Big data requires storage and in a huge manner. Data storage solutions can be in the cloud, on-premises, or both. Data can be stored in any form and bring desired processing requirements and necessary process engines to those data sets on an on-demand basis. The cloud is gradually gaining popularity because it supports current compute requirements.
3. Research
Explore the data further to make new discoveries. Share your findings with others.
4. Analysis
The next important thing is to analyze the data and act on the data. With modern tools, we get new clarity with a visual analysis of your varied data sets. Build data models with machine learning and artificial intelligence. Put your data to work.
Benefits of Big data
- Big data makes it possible to gain more complete answers because of the more information.
- Big data plays a critical role in developing effective risk management processes and strategies.
- The large volume of data collected helps businesses identify what fits their customer base. Information on what others think of your products/services can help in product development.
- More complete answers mean more confidence in the data which means a completely different approach to tackling problems.
Challenges in Big data
While big data holds a lot of promise, it is not without its challenges. Although new technologies have been developed for data storage, data volumes are doubling in size about every two years. Organizations still struggle to keep pace with their data and find ways to effectively store it.
It’s not enough to store the data. Clean data, or data that are relevant to the client and organized in a way that enables meaningful analysis, requires a lot of work. Data scientists spend 50 to 80 percent of their time curating and preparing data before it can actually be used.
Big data technology is changing at a rapid pace. A few years ago, Apache Hadoop was the popular technology used to handle big data, latter Apache Spark was introduced. Today, a combination of the two frameworks appears to be the best approach. Keeping up with big data technology is an ongoing challenge.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed big data and the 3 V’s of Big data. We have also discussed the working of big data and the challenges faced in it. The big data and analytics benefits prove how powerful a tool it has emerged to be for businesses irrespective of size and capacity.
Thank you for visiting our website.
Also Read:
- Flower classification using CNN
- Music Recommendation System in Machine Learning
- Top 15 Python Libraries For Data Science in 2022
- Top 15 Python Libraries For Machine Learning in 2022
- Setup and Run Machine Learning in Visual Studio Code
- Diabetes prediction using Machine Learning
- 15 Deep Learning Projects for Final year
- Machine Learning Scenario-Based Questions
- Customer Behaviour Analysis – Machine Learning and Python
- NxNxN Matrix in Python 3
- 3 V’s of Big data
- Naive Bayes in Machine Learning
- Automate Data Mining With Python
- Support Vector Machine(SVM) in Machine Learning
- Convert ipynb to Python
- Data Science Projects for Final Year
- Multiclass Classification in Machine Learning
- Movie Recommendation System: with Streamlit and Python-ML
- Getting Started with Seaborn: Install, Import, and Usage
- List of Machine Learning Algorithms
- Recommendation engine in Machine Learning
- Machine Learning Projects for Final Year
- ML Systems
- Python Derivative Calculator
- Mathematics for Machine Learning
- Data Science Homework Help – Get The Assistance You Need
- How to Ace Your Machine Learning Assignment – A Guide for Beginners
- Top 10 Resources to Find Machine Learning Datasets in 2022
- Face recognition Python
- Hate speech detection with Python

